Osteoarthritis of the knee — progressive-degenerative-degenerative diseases malocclusion. Initially affects the cartilage tissue, and therefore in a destructive process involved bony structures.
The causes of the development of osteoarthritis become elevated of physical activity, insufficient physical activity, metabolic and endocrine disorders. The main clinical manifestations of malocclusion — the pain, the growing when you are walking, functional insufficiency of the knee and its deformation. As the progression of osteoarthritis develops ankylosis (total or partial immobilization of the joint). When you make a diagnosis orthopedic focuses on the results of instrumental examinations — arthroscopy, x-ray, CT scan, magnetic RESONANCE imaging. In the treatment of osteoarthritis of 1 and 2 degree of severity are used interactions medications, physical THERAPY, perform massages and physiotherapy treatments. The ineffectiveness of conservative therapy or to identify the malocclusion in the final stage of a patient prepare for the restoration of the knee.
The characteristics of the disease
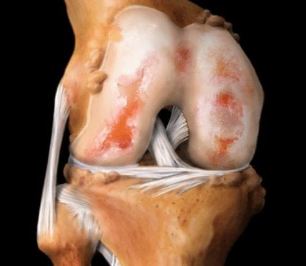
Osteoarthritis of the knee (gonarthrosis) — one of the most frequently diagnosed disorders affecting this joint. Under the influence of external or internal negative factors in the cartilage tissue occurs a deficiency of nutrients. The result is broken trophic, slows down the regeneration of connective tissue structures. Is premature aging of the hyaline cartilage. He is thin, crêpe, becomes rough, loses its strength, firmness and elasticity. Cartilage tissue can no longer perform its main function — reduction of friction in the joints of the bones. Subchondral bone exposed, compacted, and they occur osteosclerotic changes. To stabilize the knee joint during the journey they grow, they flatten the edge plates of bone with formation of osteophytes (bone outgrowths).
Osteophytes in the knee joint.
Primary osteoarthritis initially affects the healthy hyaline cartilage due to congenital reduce their functional resistance. Malocclusion secondary occurs when already available defects of the cartilage tissues. They can be triggered by previous injuries in the knee, an inflammatory process, completely aseptic necrosis, hormonal changes, disorders of the metabolism.
| Clinical-radiological stage of osteoarthritis of the knee | Particular signs |
| The first | The mobility of the knee is slightly decreased, the contours of the joint space become indistinct, a bit narrow. On the edges of the bony plates we observe the formation of a small amount of osteophytes |
| The second | Flexion or extension of the knee feels a crunch, clicks, and crackling. The muscles moderately atrophy, significantly reduced the articular slit formed in a significant amount of osteophytes, on bone tissue is detected osteosclerosi subchondral |
| The third | The knee joint is deformed, drastically limited mobility. We see, in total or in part, the remodeling of the joint space, a large number of outgrowths of bone, subchondral cyst, pathologic formations, move freely in the cavity of the joint |
Causes and triggers
Impetus to the development of destructive-degenerative process in hyaline cartilage usually becomes several negative factors. The cause of the development of osteoarthritis of the knee in childhood and adolescence are violations of training ligamentous sheath of the tendon of the machine, high-grade dysplasia. This, in turn, due to a hereditary predisposition. Cause the destruction of the cartilage can variety of injury — fractures, severe bruises, sprains, partial or total retinal tears of the ligaments, muscles, tendons, meniscus. The excessive load on the joint and cause the development of malocclusion. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis develops through several (3 to 5) years after the damage of the connective tissue or of the bony structures. The malocclusions can occur after surgery. And the cause becomes the incompetence of doctors, and the considerable damage of the cartilage and its regeneration delayed. The appearance of the disease also predispose to the following factors:

- the excess of body weight, in which almost all structures of the musculoskeletal system, and especially the knees, are overweight cargoes;
- excessive physical activity, often linked to the microtraining of the cartilage tissue and further progression of destructive processes;
- sedentary life-style, which is deteriorating the blood flow in the legs and form a nutrient deficiency in the hyaline cartilage;
- system inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic malocclusion — rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, gout, osteoporosis, systemic lupus erythematosus.
The clinical picture
In the majority of cases of osteoarthritis of the knee is manifested deaf, dumb pain after regular exercise. The reason of his presence becomes irritating osteophytes on the adjacent soft tissues, venous stasis, intra-articular hypertension, muscle spasms. Osteoarthritis is characterized by "starting" the pain, which appears due to the swelling of the joint or reactive synovitis. When a person for a long time in a sitting position, and then rises, when the first steps you feel some pain. There are the so-called "siege" pain periodic character. The joints of the knee when walking "wedges" as a result of crushing of parts of the damaged cartilage tissues between the two surfaces of the joint. Also in osteoarthritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- crackles lung, or scrunch in flexion or extension of the knee, arising in the case of displacement of the bony structures with regard to each other in the background Antoniushof cartilage;
- stiffness, an event that grows as remodeling of the joint space;
- spasms of the muscles located in the area of the knee, usually appear to reduce the pain;
- deformation of the joint, caused destructive changes to subchondral bone.
With osteoarthritis the person difficult to climb the stairs and go for long walks because of the constant knee pain. For malocclusion often complicated synovitis — inflammation of synovial skin. Clinically manifest training rounded elastic seal, hyperemia, strong swelling, increased body temperature up to 37,1—38 °C. In the absence of an intervention by arthritis complicated a spontaneous hemarthrosis (bleeding into the cavity of the knee), partial or total loss of mobility, osteonecrosis femoral condyle, external subluxation places of interest such as the patella.
Diagnostics
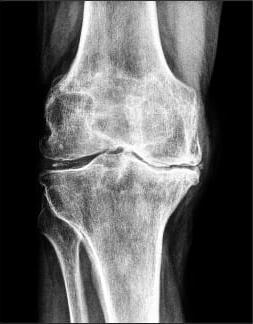
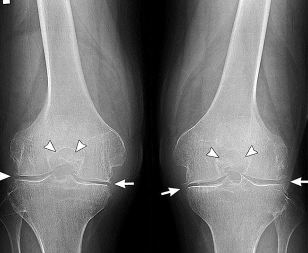
The clinical picture of osteoarthritis, particularly complicated synovitis, quite similar with the symptoms of many inflammatory diseases diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Then is made the differential diagnosis to rule out arthritis, tendonitis, of tendovaginitis. With the help of search tools that defined the state of the knee joint and its degree of functional activity. In the diagnosis of osteoarthritis the most informative x-ray. Of the images well visible osteophytes, thinning of the articular slit, the deformation of bone structures (cysts, osteosclerosi subchondral). Symmetric reduction of the joint space of the knee joints affected by osteoarthritis. Likely, work will need to both arts. More details to evaluate the changes in the hyaline cartilage help of ULTRASOUND, mri, CT. Research is conducted to identify inflammatory or degenerative lesions of the soft tissues, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. If necessary, is performed arthroscopy — minimally invasive surgical manipulation. During the course of a diagnostic procedure are the inner surface of the joint, is made a fence of biomaterials — sheaths, synovial, joint fluid, cartilage tissues. When synovitis by the sting extract pathological exudate as to improve the well-being of the patient and for the study of its composition.
The tactic of treatment
Osteoarthritis of the knee 1 gravity quite well-suited to therapy with the physical activity, prolonged use of chondroprotectors. Usually does not require the use of pain killers, as well as the symptoms expressed are not brilliant or completely absent. With osteoarthritis of the knee grade 2 is also on the conservative treatment. But if the disease progresses or diagnosed with the destruction of a considerable amount of cartilage tissues, which is in the course of a surgical intervention, usually surgery. In some cases, the patients showed arthrodesis — artificial analogue of ankylosis, or complete immobilisation of the knee.
Drug therapy
Sick of arthritis, 2 or 3 degrees with the first days of treatment is recommended to wear rigid or semi-rigid orthosis, substantially restrict mobility of the knee. With a mild damage to the cartilage, it is sufficient to use elastic springs of the drums — knee usd. Close the joint, feel the further destruction of the tissues. Patients should reduce the motor activity, do not lift weights, avoid a long walk. Are assigned to physical therapy (5-10 sessions) to improve the blood circulation in the knee and stimulate the regeneration of connective tissue structures:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- electrotherapy high frequency;
- electrophoresis with anesthetics and protectors of the cartilage;
- application with ozokerite and (o) of paraffin wax.
Strengthen the musculo-ligamentous machine and improve the motor function of the knee will help only regular therapeutic exercise. Medical THERAPY collects exercises individually for each patient, taking into account the degree of osteoarthritis and physical preparation. The first training sessions under its control. When the arthritis is strictly prohibited any type of heavy traffic. You will improve the circulation of the blood, but also to cause still more mikrotemperaturnye cartilage. The movements must be smooth, measured, with a small amplitude. In the initial stage of knee osteoarthritis occurred destructive changes to the cartilage, it is possible to solve with only physiotherapy. Well, it is well-established § irudoterapia, or medical care of the leech. In the absence of signs in the municipality are placed 3-4 leeches, usually in the region of the places of interest such as the patella. Annelids bite the skin and inject in the blood and saliva with a huge amount of biologically active substances.
Pharmacological agents
For the resolution of severe pain in the knee you place drugs block with glucocorticosteroids. Hormonal funds usually combined with anesthetics. Intra-articular injection with osteoarthritis are performed only when absolutely necessary, as well as for corticosteroids, the characteristic of the expressed events. More often in the treatment of osteoarthritis is to apply non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in a variety of dosage forms:
- solutions for parenteral administration;
- pills;
- creams and gel.
In the regimens included are necessarily chondroprotectors in the form of injection or pills. These funds stimulate the regeneration of cartilage worn, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic effect, anti-edema. Any knee pain should be a signal for immediate treatment for the orthopedic technician. Timely manner, spent for the treatment of osteoarthritis will prevent the development of serious complications -and, in some cases, warns the disability of the patient.

















































